Key Highlights:
- Excavators, also known as diggers, are heavy machinery designed for excavating, lifting, and moving soil and materials.
- Key components of an excavator include the boom, dipper, bucket, cab, hydraulic system, and tracks or wheels.
- Modern excavators can reach average digging depths of up to 20 feet, improving construction efficiency and safety.
- Types of excavators include crawler, wheeled, mini, long reach, and suction machines, each suited for specific applications.
- Crawler excavators excel in rough terrain, while wheeled diggers offer mobility in urban settings.
- Mini diggers are compact for small-scale projects, and long reach diggers are designed for deep excavation tasks.
- Excavators are increasingly being equipped with automation technologies for remote operation and performance monitoring.
- The history of excavators dates back to the steam shovel in 1796, with significant advancements in hydraulic technology occurring in the late 19th century.
- Current trends indicate a growing demand for technology-driven and environmentally sustainable excavators in the construction sector.
Introduction
Excavators serve as the backbone of the construction industry, showcasing the strength and versatility essential for demanding tasks such as excavation, demolition, and material handling. These robust machines go beyond mere brute force; they incorporate advanced technology and a range of attachments that significantly enhance their functionality, making them vital on contemporary job sites. As the need for innovative and efficient earthmoving solutions continues to rise, it prompts an important question: how do excavators adapt to meet the challenges posed by the ever-evolving landscape of construction and infrastructure development?
Define the Excavator: Understanding Its Core Functionality
A digger exemplifies what is an excavator machine, as it is a robust piece of heavy machinery specifically designed for excavating, lifting, and moving substantial amounts of soil and materials. It consists of a boom, dipper (or stick), bucket, and a cab mounted on a rotating platform known as the house. In modern construction projects, understanding what is an excavator machine is essential, as excavators play a crucial role in various tasks, including trenching, demolition, and material handling. Their versatility is further enhanced by the ability to equip them with various attachments, enabling specialized functions such as grading or lifting heavy loads.
In 2026, diggers are recognized for their significant contributions to construction efficiency, with contemporary models capable of reaching average digging depths of up to 20 feet, depending on the configuration. This capability is essential for projects that require deep foundations or extensive trenching. Industry experts emphasize that diggers not only streamline processes but also improve safety and efficiency at work sites. As one industry leader remarked, 'What is an excavator machine? It serves as the backbone of any major construction project, enabling us to tackle complex tasks with precision and speed.' Furthermore, increasing public and private investment in infrastructure-spanning residential, commercial, industrial, mining, and oil & gas projects-heightens the demand for digging equipment.
Key characteristics of diggers include:
- Advanced hydraulic systems that provide strong lifting capabilities
- Enhanced maneuverability for navigating confined spaces
- Options for electric or hybrid models that align with sustainability goals
The current trend toward automation in diggers is also noteworthy, with many new models featuring technology that allows for remote operation and performance monitoring, further optimizing construction processes. As the demand for effective and environmentally sustainable building solutions grows, earthmoving machinery remains at the forefront of industry innovation.
Trace the History and Evolution of Excavators
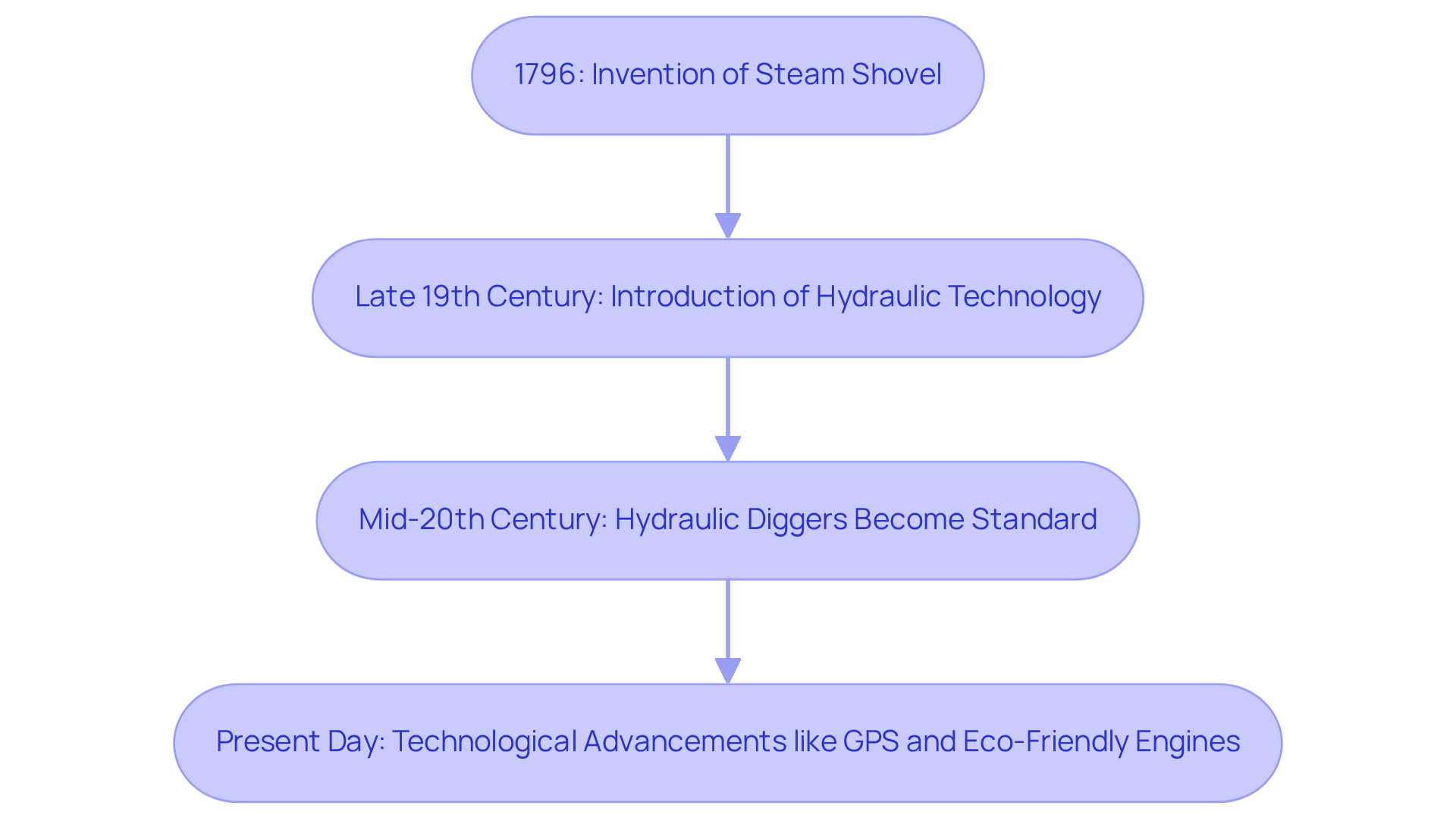
The history of digging machines can be traced back to the late 18th century, specifically with the invention of the steam shovel by James Watt and Matthew Boulton in 1796. This pioneering machine established a foundation for subsequent advancements in earthmoving equipment. A significant turning point occurred in the late 19th century with the introduction of hydraulic technology, which led to the creation of more efficient and powerful digging machines. By the mid-20th century, hydraulic diggers had become the industry standard, offering enhanced performance and versatility.
Today, digging machines continue to evolve, driven by technological advancements such as the integration of GPS systems and eco-friendly engines. These innovations not only enhance operational efficiency but also contribute to reducing environmental impact. The ongoing development in this field underscores the commitment to improving equipment reliability and service quality, ensuring that modern digging machines meet the demands of various applications.
Explore Different Types of Excavators and Their Applications
Excavators play a crucial role in construction, with various types designed for specific applications:
-
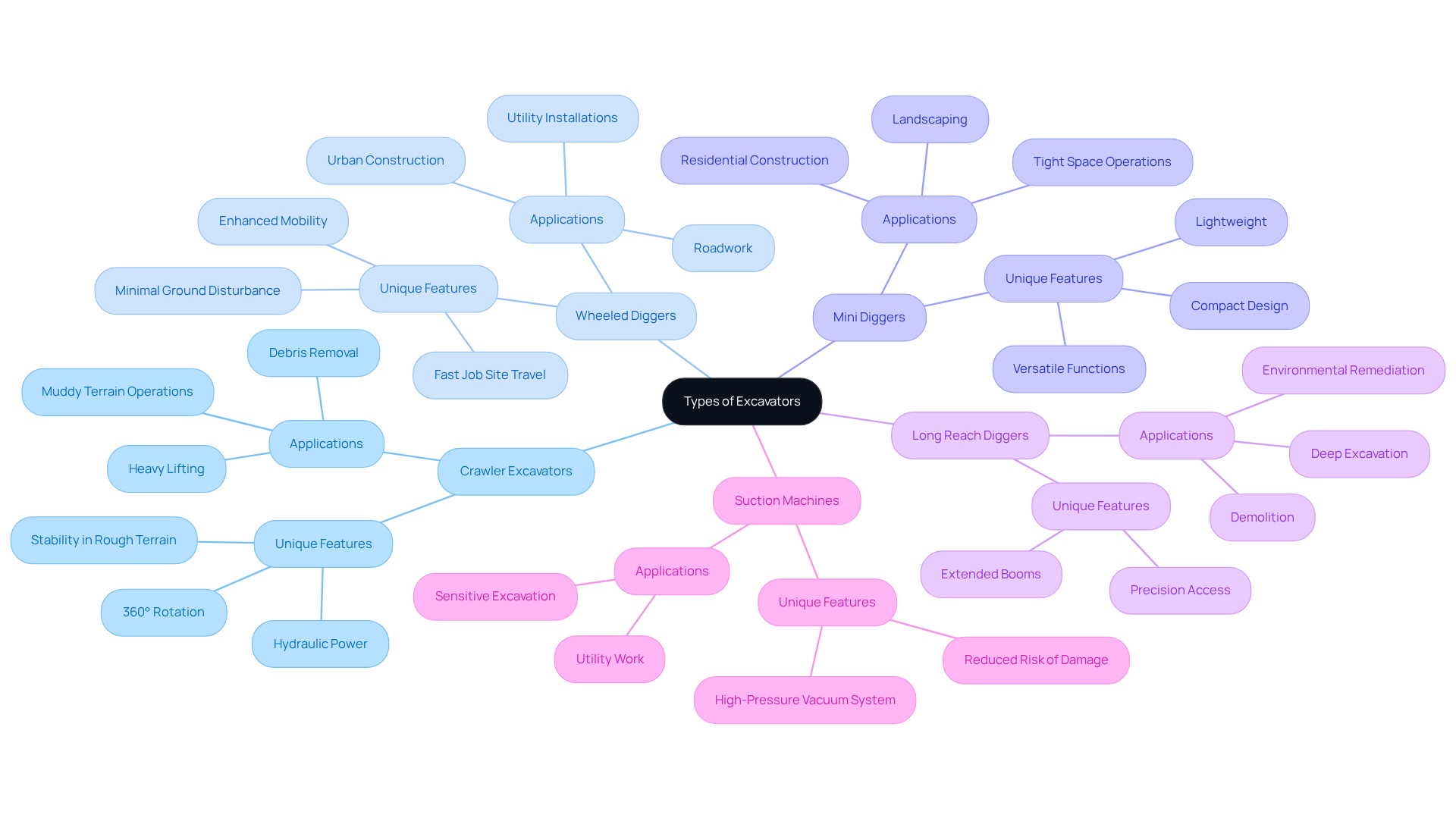
Crawler Excavators: These machines, equipped with tracks, excel in rough terrain and heavy lifting tasks. Their hydraulic power allows for a full 360° rotation, making them versatile for operations such as digging and debris removal. Crawler diggers are particularly effective in muddy conditions, providing stability and safety during heavy-duty construction. Their capacity to handle substantial loads in challenging environments makes them a preferred choice.
-
Wheeled Diggers: Offering enhanced mobility, wheeled diggers are ideal for urban settings where space is limited. They can swiftly travel between job sites without needing trailers, which minimizes downtime. These machines are favored for tasks that require speed and minimal ground disturbance, such as roadwork and utility installations, making them popular among contractors in densely populated areas.
-
Mini Diggers: Compact and versatile, mini diggers are suited for small-scale projects and tight spaces. Their lightweight design allows them to operate in confined areas, making them perfect for residential construction and landscaping tasks. Capable of performing various functions, including trenching and material loading, mini diggers are invaluable in urban settings. The market for mini and mid-sized diggers is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.1% from 2025 to 2032, reflecting their increasing demand.
-
Long Reach Diggers: Designed for deep excavation and demolition, these machines feature extended booms that provide access to hard-to-reach locations. They are commonly utilized in large-scale construction and environmental remediation projects, where precision and reach are essential. Their specialized design enables them to perform tasks that standard diggers cannot.
-
Suction Machines: Utilizing high-pressure vacuums, suction machines are specialized for careful digging, particularly near sensitive underground utilities. They significantly reduce the risk of damaging existing infrastructure, making them a preferred choice for utility work. This technology is increasingly vital as urban infrastructure expands.
Choosing between crawler and wheeled machinery often depends on the specific needs of a project. Crawler machines are preferred for their stability and heavy lifting capabilities, while wheeled models are selected for their speed and ease of movement in urban environments. As the construction sector evolves, trends indicate a growing preference for technology-driven diggers that enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime. Industry insights suggest that the Asia Pacific region is expected to reach a market value of $10.0 billion by 2032, underscoring the global demand for these machines. Construction project supervisors emphasize the importance of selecting the right digging machine for specific jobs, ensuring projects are completed efficiently and effectively.
Identify Key Components and Features of Excavators
Excavators consist of several essential components that work together to execute tasks efficiently:
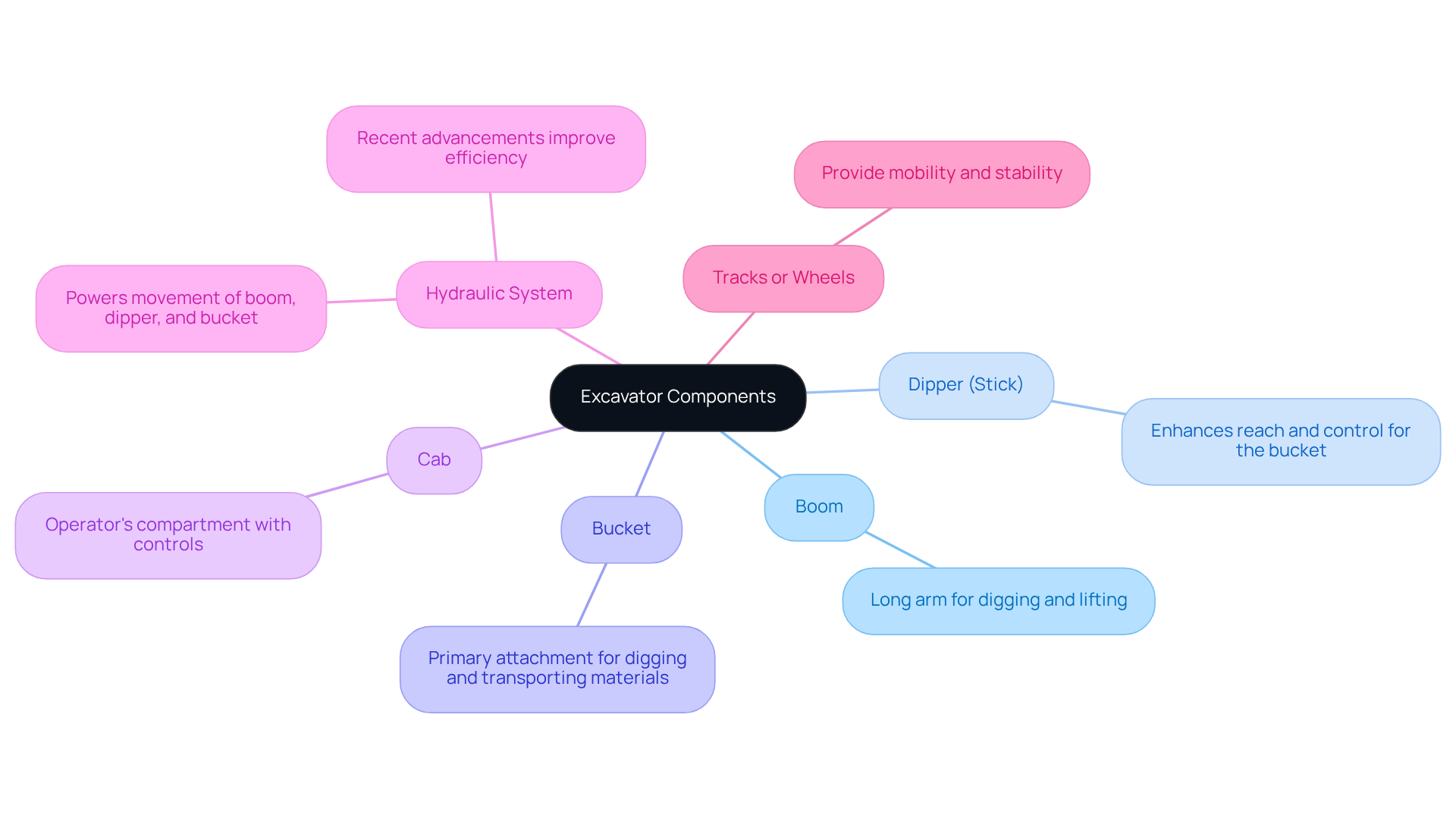
- Boom: This long arm extends from the excavator's house, enabling effective digging and lifting operations.
- Dipper (Stick): Attached to the boom, the dipper enhances reach and control for the bucket, allowing for precise material handling.
- Bucket: The primary attachment for digging and transporting materials, available in various shapes and sizes tailored for specific tasks.
- Cab: The operator's compartment, equipped with controls for maneuvering the digging machine and monitoring its functions, ensuring safety and efficiency.
- Hydraulic System: A vital component that powers the movement of the boom, dipper, and bucket. This system generates the necessary force for heavy lifting and digging, significantly impacting operational efficiency. Recent advancements in hydraulic technology, such as those observed in Volvo machinery, have enhanced responsiveness and fuel efficiency, with some models providing up to 15% improved performance compared to earlier versions.
- Tracks or Wheels: Depending on the type of digger, these provide mobility and stability across various terrains, enhancing the machine's versatility.
Understanding what is an excavator machine and its components is crucial for operators and project managers, as this knowledge informs maintenance practices and optimizes operational efficiency. Consistent upkeep of the hydraulic system, involving prompt inspections and compliance with service timelines, can prolong the lifespan of digging machines. Mini diggers, for instance, typically last around 7,000-10,000 hours, and with proper care, many machines can reach over 10,000 operational hours. As Danny Freeman, Sales Training and Product Support Manager, emphasizes, integrating power, precision, and efficiency into hydraulic technology is essential for maximizing excavator performance.
Conclusion
An excavator machine stands as a cornerstone in the construction industry, facilitating efficient excavation, lifting, and material handling. Its robust design, featuring a boom, dipper, bucket, and a rotating house, highlights its essential role across various applications, from trenching to demolition. For industry professionals, understanding the functionality and significance of excavators is crucial, as these machines are increasingly pivotal in modern construction projects.
This article has highlighted key insights, including the evolution of excavators from the steam shovel to today's advanced hydraulic systems. The discussion on different types of excavators - such as crawler, wheeled, mini, and long-reach diggers - demonstrates their specialized applications tailored to diverse project needs. Furthermore, the integration of automation and eco-friendly technologies reflects the industry's commitment to innovation and sustainability, ensuring that excavators remain at the forefront of construction equipment.
As the demand for effective and environmentally responsible construction solutions continues to grow, recognizing the importance of excavators becomes imperative. Industry stakeholders should prioritize selecting the right type of excavator for specific tasks to enhance operational efficiency and project outcomes. Embracing advancements in excavator technology not only improves productivity but also aligns with broader goals of sustainability and safety in the construction sector.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an excavator machine?
An excavator machine, often referred to as a digger, is a robust piece of heavy machinery designed for excavating, lifting, and moving substantial amounts of soil and materials.
What are the main components of an excavator?
An excavator consists of a boom, dipper (or stick), bucket, and a cab mounted on a rotating platform known as the house.
What tasks are excavators commonly used for in construction?
Excavators are used for various tasks including trenching, demolition, and material handling.
How deep can modern excavators dig?
Contemporary excavators can reach average digging depths of up to 20 feet, depending on their configuration.
What are some key characteristics of modern excavators?
Key characteristics include advanced hydraulic systems for strong lifting capabilities, enhanced maneuverability for navigating confined spaces, and options for electric or hybrid models that align with sustainability goals.
How is automation impacting excavators?
Many new excavator models feature technology that allows for remote operation and performance monitoring, optimizing construction processes.
Why is the demand for excavators increasing?
The demand for excavators is increasing due to rising public and private investment in infrastructure projects across residential, commercial, industrial, mining, and oil & gas sectors.
What role do excavators play in construction efficiency?
Excavators streamline construction processes and improve safety and efficiency at work sites, serving as the backbone of major construction projects.
List of Sources
- Define the Excavator: Understanding Its Core Functionality
- Excavators Market Size, Share, Trends | Growth Report [2032] (https://fortunebusinessinsights.com/industry-reports/excavators-market-100861)
- Excavator Market Size, Share & 2030 Growth Trends Report (https://mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/global-excavator-market)
- Excavator Market Size: In-Depth Analysis (https://introspectivemarketresearch.com/reports/excavator-market)
- Crawler Excavator Market Size, Share & Forecast Analysis - 2032 (https://gminsights.com/industry-analysis/crawler-excavator-market)
- Excavator Market Size, Share, Growth & Trends Report 2030 (https://grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/excavators-market)
- Trace the History and Evolution of Excavators
- A Brief History of Excavators (https://plant-planet.co.uk/a-brief-history-of-excavators)
- The First Hydraulic Excavators (https://oemoffhighway.com/fluid-power/article/12022256/historical-construction-equipment-association-hcea-the-first-hydraulic-excavators)
- A brief history of the Excavator (https://highways.today/2022/11/23/history-excavator)
- 10 Years of Innovation: Hydraulic Excavators Have Come a Long Way (https://oemoffhighway.com/market-analysis/trends/blog/21319526/10-years-of-innovation-hydraulic-excavators-have-come-a-long-way)
- Explore Different Types of Excavators and Their Applications
- Mini and Mid Excavators Market Size, Share | Forecast 2032 (https://kbvresearch.com/mini-and-mid-excavators-market)
- The 7 Types of Excavators: How to Choose an Excavator (https://micoequipment.com/blog/7-types-of-excavators)
- Top-Selling Mini Excavators in 2024 (https://equipmentworld.com/market-pulse/article/15682045/topselling-mini-excavators-in-2024)
- The Different Types of Excavators (https://customtruck.com/blog/different-types-of-excavators-2)
- Excavators Market Size, Share, Trends | Growth Report [2032] (https://fortunebusinessinsights.com/industry-reports/excavators-market-100861)
- Identify Key Components and Features of Excavators
- 22 Parts of an Excavator - BigRentz (https://bigrentz.com/blog/parts-of-excavator?srsltid=AfmBOooQbOmVLjIYk_QWMPDCUBbRd7XpzSI9iCpIgs--wdInm51uOnTc)
- Exploring the Anatomy of an Excavator: A Guide to Its Essential Parts (https://dozr.com/blog/parts-of-an-excavator)
- Understanding Excavator Hydraulic Systems | The Scoop (https://volvoce.com/united-states/en-us/resources/blog/2025/understanding-excavator-hydraulics-part-1)
- How Long Do Excavators Last? Equipment Lifespan Guide (https://wwcm.com.au/excavator-lifespan-guide)
- 10 Parts of an Excavator + Bonus FAQs (https://gregorypoole.com/main-parts-of-excavator)




