Overview
Best practices for ozone rental focus on effective odor elimination while ensuring safety and health. The article outlines essential guidelines such as pre-usage preparation, proper ventilation, and adherence to safety measures to maximize the efficacy of ozone generators, emphasizing the importance of responsible usage to mitigate potential health risks associated with ozone exposure.
Introduction
In the quest for a fresher, cleaner environment, ozone generators have emerged as powerful tools for odor elimination and pathogen control. These devices harness the potent oxidizing properties of ozone to break down unpleasant odors at their source, making them particularly effective in spaces affected by smoke, mold, or pet dander.
However, the effective use of ozone generators comes with its own set of challenges and considerations. Understanding how these machines work, implementing best practices, and adhering to safety precautions are crucial for maximizing their benefits while minimizing health risks.
This article delves into the intricacies of ozone technology, dispelling common misconceptions and providing practical troubleshooting tips to ensure users can achieve optimal results in their odor management efforts.
Understanding Ozone Generators: How They Work for Odor Elimination
Ozone generators are specialized devices designed to create O3, a powerful oxidizing substance famous for its capacity to eliminate smells efficiently. The operational mechanism involves the use of either a corona discharge or ultraviolet light to decompose oxygen molecules (O2) in the air, resulting in the creation of triatomic oxygen. When the gas meets materials responsible for unpleasant smells, it reacts chemically, breaking them down into less fragrant compounds.
This ability renders air purifiers especially advantageous in settings afflicted by constant smells, such as those caused by smoke, mold, and pet dander. Recent research indicates that in mouse bedding studies, the presence of eight species of pathogens was significantly reduced to three after just 60 minutes of treatment with a specific gas, demonstrating its efficacy not only in scent removal but also in pathogen control.
Comprehending the intricacies of this gas's mechanism is crucial; improper usage can lead to inadequate odor removal or even hazardous exposure levels for humans and pets. Paul Honess emphasizes the significance of funding acquisition for research and development in this area, highlighting the necessity for ongoing innovation in atmospheric technology to ensure its safe and effective use. Furthermore, the relationship between oxygen concentration and contact time is critical for effective viral inactivation, allowing for tailored disinfection strategies that can be particularly beneficial in construction settings.
Furthermore, a case study titled 'PCR Testing of Media Placed in Soiled Bedding for Mouse Colony Health Surveillance' demonstrates the practical application of a specific treatment, highlighting its effectiveness in early pathogen detection and control. Therefore, it is imperative to operate these machines in unoccupied spaces and ensure adequate ventilation during and after treatment. By adhering to these guidelines, users can enhance the advantages of air purifiers while reducing health hazards, establishing them as a crucial instrument for efficient odor remediation.
Best Practices for Using Ozone Generators Effectively
To utilize the complete capability of air purifiers, it's crucial to follow these best practices:
-
Pre-usage Preparation: Before using the device, ensure that the area is clear of any materials that could react adversely with oxygen, particularly certain rubber and plastic products. Additionally, it's crucial to vacate the space, including pets, to mitigate health risks associated with exposure to certain gases.
-
Ventilation: Operate the machine in an adequately ventilated environment to facilitate the circulation of fresh air after treatment. This practice is essential for reducing residual gas concentration levels.
-
Duration and Timing: Adjust the generator's runtime based on the size of the treatment area and the strength of the smells. Generally, a few hours suffices for most residential applications, although particularly strong odors may necessitate extended operation.
For instance, fresh-cut green bell peppers treated with 1.8 mg L of ozonated water achieved Brix values of 4.25°, illustrating the effective application of this gas in enhancing food quality.
-
Post-treatment Procedures: Following treatment, ensure thorough ventilation of the area before re-entry. If possible, measure air quality levels to confirm they are within safe limits before allowing people or pets back into the space. Significantly, for sensorial attributes, control, NaClO, and HO-treated melon slices maintained their quality for six days, while GO-treated samples were stored for nine days with good quality, highlighting the advantages of the treatment.
-
Regular Maintenance: Frequently clean the air purifier according to the manufacturer's instructions to ensure its optimal performance. Accumulated dust and debris can hinder the production of this gas, significantly reducing its effectiveness.
By applying these best practices, users can enhance the effectiveness of air purification devices, including ozone rental options, while prioritizing safety and health issues to ensure a balanced approach to odor control.
It's also important to note that treatments involving oxygen did not significantly change TSS trends in fresh-cut tomatoes, melon fruits, and pineapple compared to untreated samples, which contextualizes the effectiveness of this method in food preservation, particularly for construction project managers involved in food-related projects.
Safety Precautions When Using Ozone Generators
When using air purification devices, following stringent safety measures is crucial to safeguard both operators and the nearby ecosystem. Here are key practices to follow:
-
Function in Vacant Areas: To prevent contact with heightened air quality issues, always operate the device in locations that are vacant.
The NIOSH recommends an upper limit of 0.10 ppm for exposure to this substance, highlighting the importance of minimizing risks.
-
Use Protective Equipment: If closeness to the machine is unavoidable during operation, don appropriate protective gear such as masks and goggles to reduce the risk of inhalation and irritation.
-
Understand Local Regulations: Familiarize yourself with local rules concerning air purification devices, as some regions impose specific guidelines and restrictions that must be adhered to. CARB is actively working to educate professionals and the public about the dangers of using air purification generators, which underscores the necessity of compliance with these regulations.
-
Establish Emergency Protocols: Be prepared for potential incidents of excessive atmospheric contamination by understanding emergency procedures, including evacuation plans and the use of air purifiers to restore safe air quality swiftly.
Significantly, this gas has been shown to achieve a remarkable 97% kill rate for airborne bacteria, viruses, and mold, as evidenced in case studies. This underscores its effectiveness as a disinfectant when used responsibly.
By prioritizing these safety measures, users can significantly reduce the risks associated with exposure while effectively benefiting from its powerful odor elimination capabilities.
Common Misconceptions About Ozone Generators
Misunderstandings regarding air purification devices can lead to improper use and health risks. Here are some prevalent misconceptions:
-
Ozone Is Safe at Any Level: Contrary to popular belief, this gas can be harmful even at levels commonly found in the United States.
Research indicates a direct connection between prolonged atmospheric pollutants and health problems, including uncontrolled asthma in adults, as noted by Jacquemin et al., who state,
The results suggest that long-term contact with pollutants is associated with uncontrolled asthma in adults, defined by symptoms, exacerbations, and lung function.
Additionally, hospital admissions related to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases have been positively associated with short-term air pollution exposure, further emphasizing the potential dangers.
-
Ozone Functions Quickly: While this substance is a potent oxidizing agent and effective in eliminating smells, it does not operate immediately. The duration needed for the gas to effectively remove smells varies greatly, particularly in extensive or heavily polluted regions, where total neutralization might require more time than expected.
-
Ozone Can Replace Cleaning: It is crucial to understand that this substance is not a stand-in for traditional cleaning methods. Ozone rental devices are most effective when utilized in conjunction with thorough cleaning practices that eliminate odor sources. Furthermore, the APHENA study has found positive links between short-term pollutant contact and all-cause, cardiovascular, and respiratory mortality, which emphasizes the urgency of addressing these misconceptions.
Awareness of these misconceptions, along with the understanding that primary exposure to this gas occurs through inhaling surrounding air influenced by various factors, can enhance the safe and effective use of these devices, ensuring project managers achieve optimal results while safeguarding health.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Ozone Generators
Users of ozone devices often face several common challenges that can hinder their effectiveness. Here are key troubleshooting steps to address these issues:
-
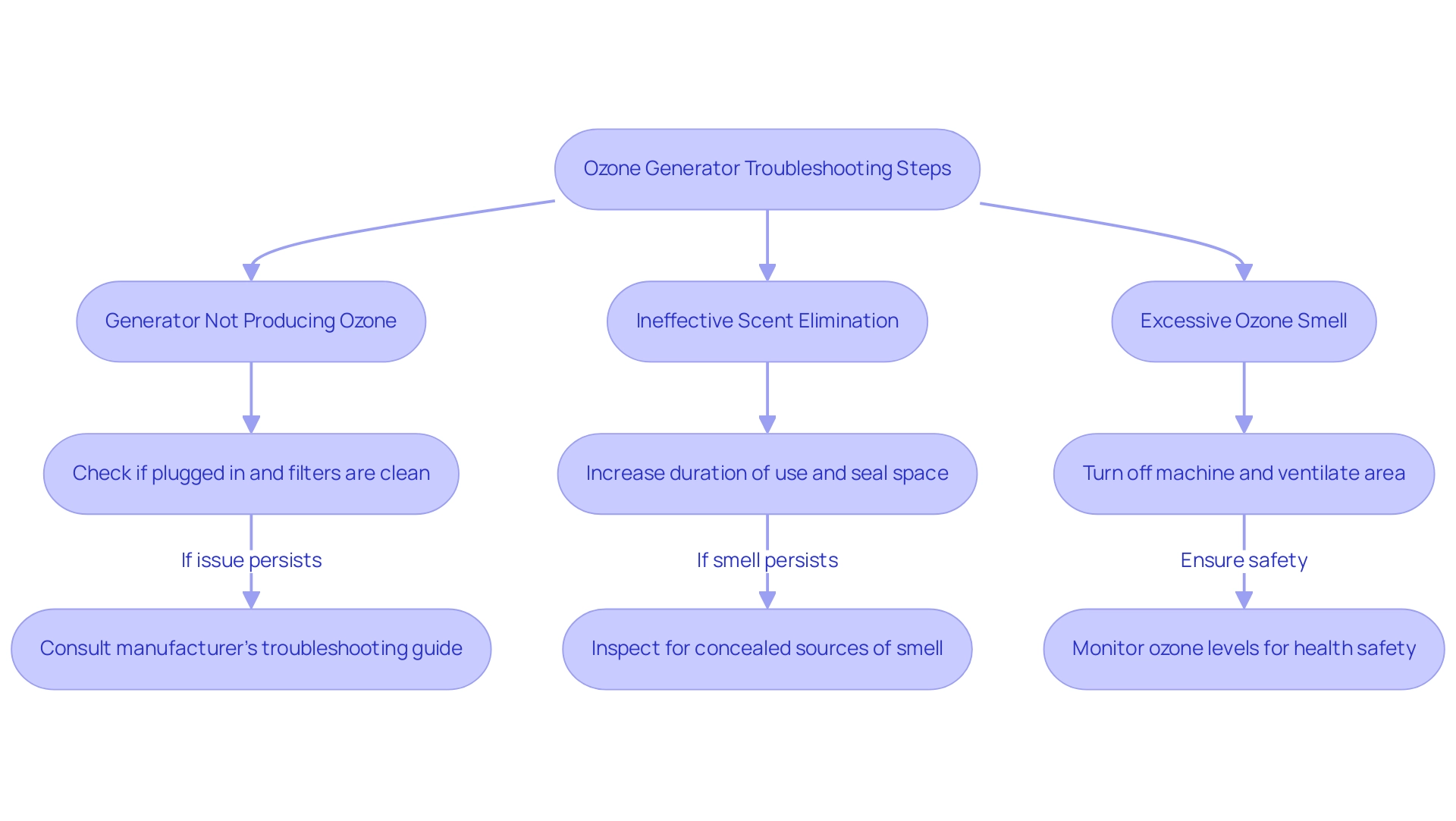
Generator Not Producing Ozone:
First, verify that the unit is plugged in correctly and that the filters are clean.
A malfunctioning generator may signal deeper issues; thus, consulting the manufacturer’s troubleshooting guide is advisable if the problem persists.
-
Ineffective Scent Elimination:
If unpleasant smells persist after treatment, consider increasing the duration of use while ensuring the space is fully sealed.
It’s also essential to inspect the area for concealed sources of smell that may need cleaning to achieve optimal results.
-
Excessive Ozone Smell:
A strong odor of the gas indicates that the generator is functioning improperly.
In such situations, it’s essential to turn off the machine right away and ventilate the area until the scent dissipates.
Continuous elevated levels can result in health issues, as indicated by epidemiological research suggesting that prolonged concentrations above the EPA’s standards of 0.08 ppm can impact respiratory health.
As noted by Devlin et al., "Over a period of several days following a single short-term exposure, inflammation, small airway obstruction, and increased epithelial permeability resolve; damaged ciliated airway epithelial cells are replaced by underlying cells; and damaged type I alveolar epithelial cells are replaced by more ozone-resistant type II cells."
By proactively addressing these common concerns and utilizing CARB certified equipment for air cleaning, users can maintain the efficiency and safety of their ozone generators, ensuring they operate effectively in their intended environments.
Conclusion
Ozone generators present a powerful solution for odor elimination and pathogen control, but their effectiveness hinges on proper usage and adherence to safety measures. Understanding how these devices work is essential, as they utilize ozone's potent oxidizing properties to neutralize odors at their source. Best practices, such as:
- Ensuring adequate ventilation
- Operating in unoccupied spaces
- Maintaining the equipment
are critical for maximizing their benefits while minimizing health risks.
Addressing common misconceptions is equally important; ozone is not harmless at any level, nor does it provide instant results. It functions best when combined with traditional cleaning methods, ensuring a comprehensive approach to odor remediation. Troubleshooting common issues, such as:
- Ineffective odor elimination
- Malfunctioning generators
empowers users to achieve optimal results and maintain a safe environment.
In conclusion, by following established guidelines and understanding the science behind ozone generators, users can harness their full potential and create cleaner, fresher spaces. Prioritizing safety and informed usage will not only enhance the effectiveness of these devices but also contribute to healthier indoor environments. Embracing this knowledge equips individuals and professionals alike to tackle odor challenges confidently and responsibly.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are ozone generators and how do they work?
Ozone generators are devices that create ozone (O3), a powerful oxidizing agent known for eliminating odors. They operate using corona discharge or ultraviolet light to decompose oxygen molecules (O2) in the air, resulting in triatomic oxygen, which reacts chemically with odor-causing materials to break them down into less fragrant compounds.
What benefits do ozone generators provide in odor removal?
Ozone generators are particularly effective in environments with persistent odors, such as those caused by smoke, mold, and pet dander. Research has shown that they can significantly reduce pathogens in environments like mouse bedding, demonstrating their efficacy in both odor removal and pathogen control.
What safety precautions should be taken when using ozone generators?
It is crucial to operate ozone generators in unoccupied spaces and ensure adequate ventilation during and after treatment to mitigate health risks associated with ozone exposure. Users should also prepare the area by removing materials that could react adversely with oxygen and vacate the space, including pets.
How should ozone generators be operated for maximum effectiveness?
Users should ensure proper ventilation, adjust the runtime based on the size and strength of odors, and conduct thorough post-treatment ventilation. Regular maintenance of the air purifier is also essential to ensure optimal performance.
What are the best practices for using ozone generators?
Best practices include: 1. Pre-usage preparation: Clear adverse materials and vacate the area. 2. Ventilation: Operate in a well-ventilated space. 3. Duration and timing: Adjust runtime based on the treatment area. 4. Post-treatment procedures: Ventilate thoroughly before re-entry. 5. Regular maintenance: Clean the unit as per manufacturer instructions.
Can ozone treatment affect food quality?
Yes, ozone treatment can enhance food quality. For example, fresh-cut green bell peppers treated with ozonated water showed improved quality, maintaining their attributes longer compared to untreated samples.
What is the significance of ongoing research and innovation in ozone technology?
Ongoing research and development are necessary to ensure the safe and effective use of ozone generators, as improper usage can lead to inadequate odor removal or hazardous exposure levels for humans and pets.




