Overview
Choosing and using a handheld trench digger involves understanding the various types available—manual, gas-powered, electric, and hydraulic—each suited for different tasks and conditions. The article provides a comprehensive guide by detailing the pros and cons of each type, along with essential tips for safe operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting, thereby ensuring users can select the most appropriate tool for their excavation needs while maximizing efficiency and safety.
Introduction
In the realm of excavation, the choice of tools can significantly impact project efficiency and safety. Handheld trench diggers come in various types, each tailored to meet specific excavation needs, from small-scale manual options to powerful gas and hydraulic models. As the demand for effective trenching solutions rises, understanding the strengths and limitations of each type becomes crucial for both professionals and DIY enthusiasts.
This article delves into the diverse landscape of handheld trench diggers, offering insights into their features, proper usage, and maintenance tips, ensuring that every digging project is approached with confidence and expertise. With the right knowledge, users can navigate the complexities of trench digging, ultimately enhancing productivity and minimizing risks on the job site.
Exploring Different Types of Handheld Trench Diggers
When selecting a handheld trench digger, it's crucial to take into account the different varieties available, each intended for particular tasks and requirements. Manual handheld trench diggers are basic tools that rely on physical effort, making them ideal for small-scale jobs. Their lightweight design enhances portability, which is a significant advantage for projects requiring quick setups.
- Pros: Cost-effective and straightforward to use, allowing for easy transport and operation.
- Cons: Labor-intensive and not suited for larger projects, which can lead to inefficiencies in time-sensitive situations.
- Gas-Powered Trench Diggers: Equipped with powerful engines, these models excel in larger and more demanding excavation tasks. Their capability to dig deep and wide trenches makes them a preferred choice in many construction scenarios. For instance, the Caterpillar C13 ACERT Tier 4 Final gas-powered digger has a fuel consumption rate of 21.3 gph, showcasing operational efficiency for extensive trenching tasks.
- Pros: Efficient for extensive trenching, enabling faster operation that can significantly enhance project timelines.
- Cons: Heavier than manual options, requiring fuel and potentially incurring higher maintenance costs, which may be a consideration for budget-conscious projects.
- Electric Handheld Trench Diggers: Powered by electricity, these diggers are quieter and more environmentally friendly, making them suitable for indoor work or noise-sensitive areas.
- Pros: Low emissions and easy to start, providing a more sustainable option for trenching needs.
- Cons: Limited by cord length, which can restrict mobility, and may not deliver the same power levels as gas models in demanding conditions.
- Hydraulic handheld trench diggers are advanced tools that utilize hydraulic power to enhance digging efficiency, particularly in difficult soil conditions. Their design allows for precise excavation in various terrains.
- Pros: High efficiency and capability to handle tough soil, making them versatile for various applications.
- Cons: Generally more expensive and may necessitate specialized training for operators, posing a barrier for some companies.
By understanding the distinct characteristics of these handheld trench diggers, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your project requirements and personal preferences.
Significantly, the market for excavation equipment is anticipated to expand, with specialists forecasting a CAGR of 5.1% in the Chinese digger rental sector alone, indicating a potential $33.3 million opportunity. This trend underscores the importance of selecting the right tools to enhance project efficiency and success. Furthermore, real-world applications, such as the use of tractor-mounted diggers by the Ukrainian Ground Forces for rapid excavation during their 2023 counteroffensive, illustrate the effectiveness and necessity of reliable digging equipment in urgent scenarios.
Essential Tips for Using Your Handheld Trench Digger
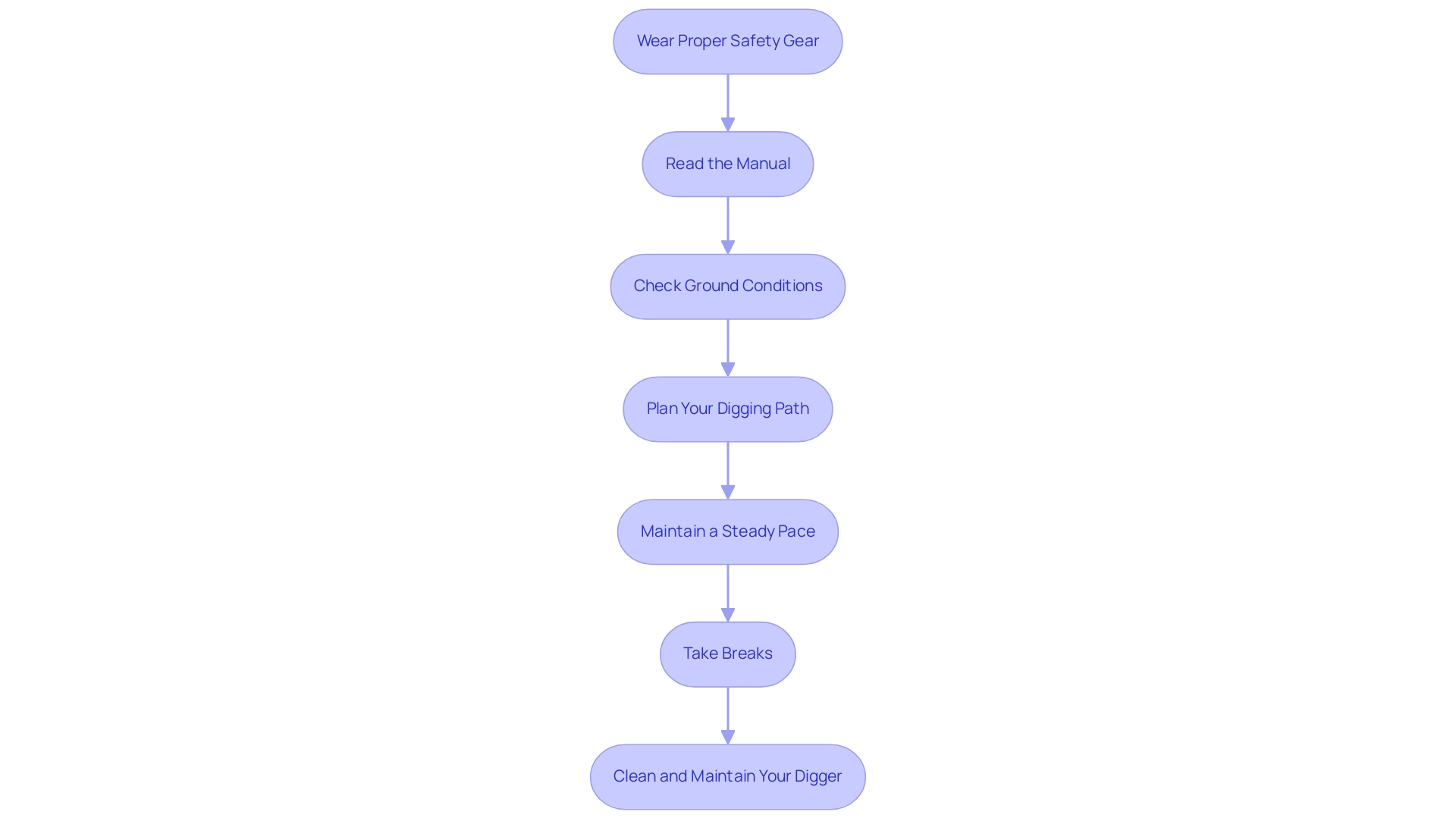
To maximize the effectiveness and safety of your handheld excavation tool, adhere to these essential guidelines:
- Wear Proper Safety Gear: Equip yourself with safety glasses, gloves, and sturdy footwear to shield against debris and potential injuries.
- Read the Manual: Familiarize yourself with the operation manual specific to your model, as it provides vital information on features, limitations, and maintenance requirements.
- Check Ground Conditions: Before commencing work, evaluate the soil type and moisture levels. It is crucial to avoid excavating in overly wet or rocky conditions unless your digger is specifically designed for such environments. This aligns with OSHA's emphasis on understanding soil characteristics to prevent cave-ins, which were a contributing factor to the 21 excavation fatalities recorded in 2017.
- Plan Your Digging Path: Clearly outline the trench path to minimize unnecessary digging and ensure compliance with designated work areas, thereby reducing risks associated with trenching.
- Maintain a Steady Pace: Operate the machine at a consistent speed, allowing it to perform its function without excessive force. This approach helps prevent tool damage and minimizes operator fatigue.
- Take Breaks: For larger tasks, incorporate regular breaks to prevent exhaustion, enabling you to maintain focus and efficiency throughout the work.
- Clean and Maintain Your Digger: After each use, thoroughly clean the tool and perform necessary maintenance as indicated in the manual. Routine maintenance not only prolongs the lifespan of your excavation equipment but also guarantees peak performance.
Moreover, the NIOSH Update 93-110 emphasizes the significance of these safety protocols by underscoring the dangers of excavation collapses and offering suggestions for prevention. By incorporating these safety tips into your routine, you can improve both efficiency and safety while using a handheld excavator, paving the way for smoother and more successful execution. Furthermore, understanding and adhering to OSHA's revised excavation standards will ensure that you are employing the best practices for soil classification and employee protection methods.
Preparing Your Worksite for Digging
Before starting any trench excavation task, it is crucial to carefully prepare your worksite by following these essential steps:
-
Clear the Area: Begin by removing all debris, rocks, and vegetation from the intended excavation site. This ensures that your work area is unobstructed, minimizing hazards that could lead to injuries.
-
Mark Underground Utilities: It is crucial to contact local utility companies to identify and mark any underground lines such as water, gas, or electricity. With a staggering 34.9 million Americans planning to dig without consulting 811 first, the risk of damaging critical services is substantial. Utilizing flags or spray paint to indicate the locations of these utilities can prevent costly accidents during excavation. As Tristan Brown, Deputy Administrator of the Department of Transportation’s Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration, states,
Contacting 811 a few days before excavating to have the position of buried utilities marked is the first step in finishing your task safely.
This practice is further supported by a new white paper from the Common Ground Alliance, which emphasizes the telecom industry's critical role in reversing the upward trend of damages to buried utilities, highlighting the need for collaborative efforts in damage prevention.
-
Establish a Safe Perimeter: Create a secure working zone by setting up barriers or cones around the trenching area. This practice helps protect bystanders and pets, ensuring a safe distance from potential hazards.
-
Gather Necessary Tools: Ensure that you have all the essential tools and equipment ready for use. This includes shovels, safety gear, and any additional support tools necessary for your specific project to facilitate efficient digging.
-
Review Safety Protocols: Take the time to familiarize yourself and your team with safety protocols designed for excavation. Discuss emergency procedures to follow in the event of an accident, reinforcing your commitment to a safe working environment. By thoroughly preparing your worksite, you not only enhance safety but also promote a more efficient process when using your handheld trench digger. Implementing these best practices is critical, especially in light of recent findings from the Common Ground Alliance, which highlight a concerning increase in damage to buried utilities due to excavation activities, as indicated in their revamped DIRT Report. Additionally, the Common Ground Alliance's recent acquisition of the Gold Shovel Association underscores ongoing efforts within the industry to improve damage prevention strategies. Proper preparation is the cornerstone of a successful and safe trenching operation.
Post-Digging Maintenance and Care
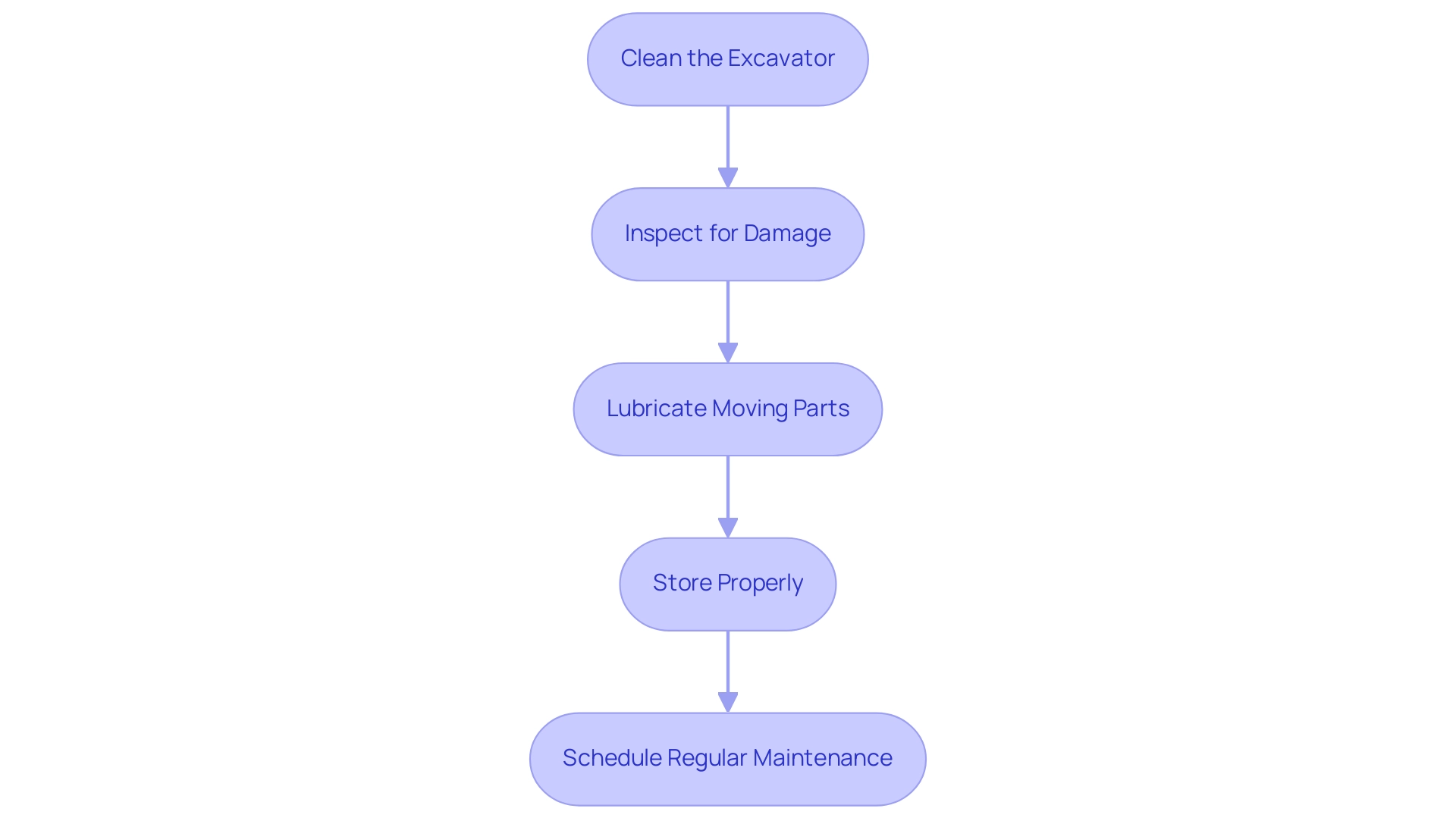
To ensure optimal performance and longevity of your handheld excavation tool, which is powered by a robust 74-horsepower Cummins engine, follow these essential maintenance steps after use:
- Clean the Excavator: Thoroughly remove dirt, mud, and debris from all components of the excavator. This simple step prevents the buildup that can impair functionality and efficiency over time.
- Inspect for Damage: Conduct a thorough inspection for any signs of wear or damage. Be vigilant for cracks, loose components, or other issues that may require immediate repair to avoid further complications.
- Lubricate Moving Parts: Carefully apply lubricant to all moving parts as specified in the manufacturer’s manual. This practice not only ensures smooth operation but also effectively guards against rust and corrosion, which is especially crucial given the vulnerabilities of diesel engines to oil oxidation and corrosion in harsh conditions.
- Store Properly: After cleaning, place the excavation tool in a dry and secure location. Protecting the equipment from outdoor elements is vital, as exposure can accelerate deterioration and reduce its lifespan.
- Schedule Regular Maintenance: Depending on your usage frequency, establish a routine for regular maintenance checks. This should include professional servicing to address any underlying issues and ensure the tool remains in peak working condition. Remember, as emphasized by industry specialists, the high expense of upkeep can greatly affect your budget, making appropriate care vital.
By adopting these post-excavation maintenance practices, you can noticeably improve the performance and longevity of your handheld trench digger, ensuring it stays dependable for upcoming tasks. According to maintenance experts, proper care can extend the average lifespan of these tools, which is critical in managing operational costs effectively.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips
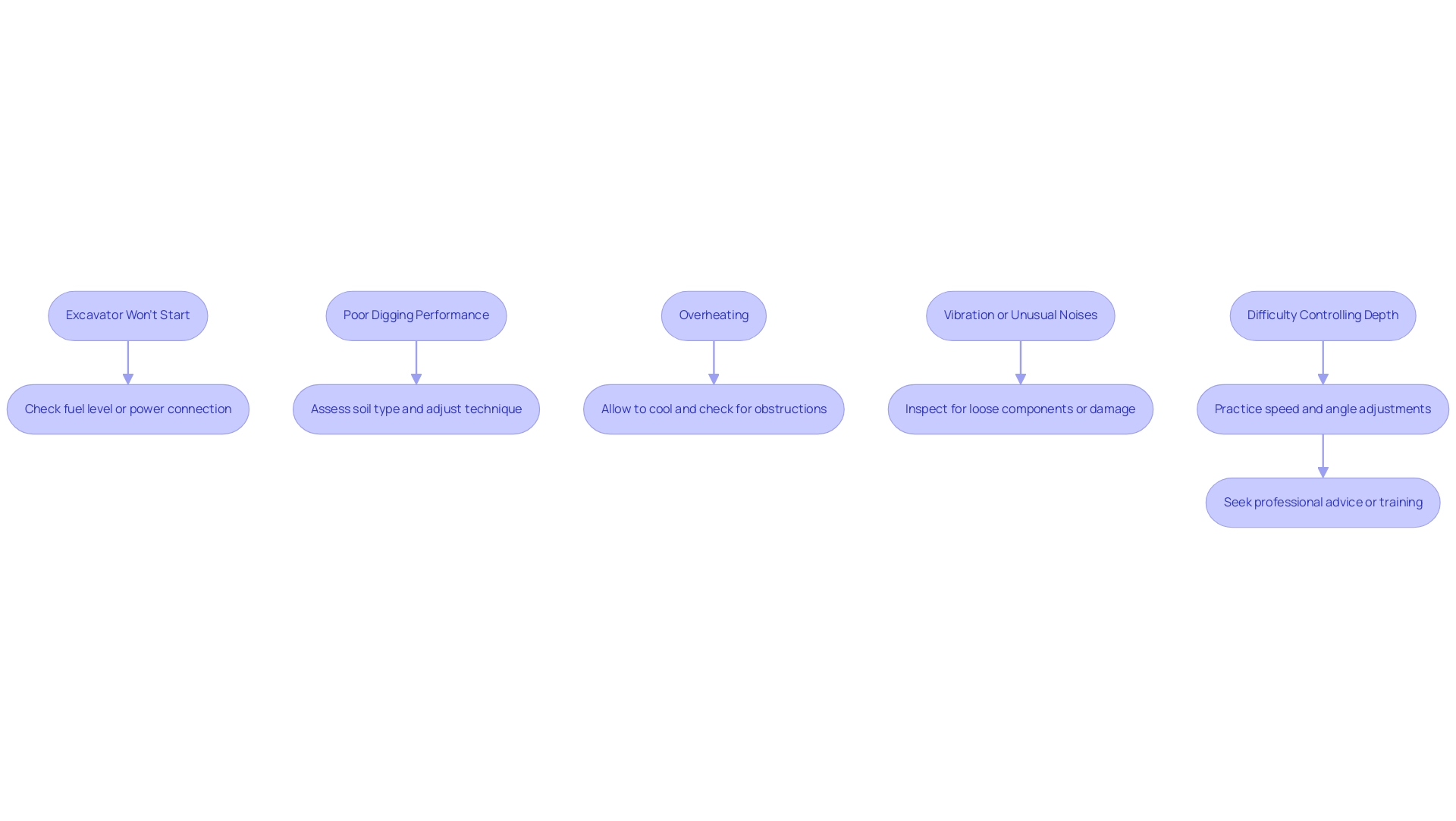
When using a handheld trench digger, encountering issues can disrupt your excavation project. Here are some common problems along with their solutions:
- Excavator Won't Start: If your excavator fails to start, first check the fuel level for gas-powered models or ensure that electric models are properly plugged in. Additionally, verify that the battery is charged and that all connections are secure.
- Poor Digging Performance: Should the excavator struggle to penetrate the soil, assess the soil type. Remember that a 48-in. boom will give you 48 in. of excavation depth at a 65-degree angle, which can help in determining if the tool is suitable for the job. It may be necessary to switch to a different type of excavator or adjust your digging technique to better suit the conditions at hand.
- Overheating: In case the excavator overheats, cease operation and allow it to cool down. Examine for any obstructions that could be hindering airflow, and ensure the excavator is free of debris that may restrict its performance. Following proper disengagement procedures, as highlighted in the case study "Completing the Trench," is essential for ensuring equipment longevity and safety.
- Vibration or Unusual Noises: If you experience excessive vibration or hear strange noises while operating the digger, stop immediately. Inspect the equipment for loose components or signs of damage, consulting the manual for further guidance.
- Difficulty Controlling Depth: To enhance your control over excavation depth, practice adjusting your speed and angle. If control issues persist, consider seeking professional advice or additional training to refine your technique. With over 60% of construction accidents occurring within an employee's first year of work, as noted by the BLS, prioritizing effective training and equipment handling is crucial for safety and operational efficiency.
Understanding how to troubleshoot these common issues is essential for maintaining productivity and ensuring a smoother digging process when using a handheld trench digger.
Conclusion
Choosing the right handheld trench digger is paramount for achieving efficiency and safety in excavation projects. As explored, the various types of trench diggers—from manual to gas-powered, electric, and hydraulic—each offer unique advantages and limitations tailored to specific project needs. By understanding these distinctions, users can select tools that best fit their excavation requirements, ensuring optimal performance and productivity.
Equally important is the proper usage and maintenance of these tools. Adhering to safety protocols, preparing the worksite meticulously, and conducting regular maintenance are all critical steps in maximizing the lifespan and functionality of a trench digger. By following essential guidelines and troubleshooting common issues, users can navigate the complexities of trench digging with confidence, ultimately minimizing risks and enhancing project outcomes.
In summary, the knowledge and application of effective trench digging techniques not only streamline the excavation process but also contribute to a safer and more successful work environment. With the right tools and practices in place, every digging project can be approached with assurance, paving the way for efficient and effective results.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the different types of handheld trench diggers available?
The main types of handheld trench diggers are manual, gas-powered, electric, and hydraulic trench diggers, each designed for specific tasks and requirements.
What are the advantages of using a manual handheld trench digger?
Manual handheld trench diggers are cost-effective, straightforward to use, lightweight, and portable, making them ideal for small-scale jobs.
What are the disadvantages of manual handheld trench diggers?
They are labor-intensive and not suited for larger projects, which can lead to inefficiencies in time-sensitive situations.
What makes gas-powered trench diggers suitable for larger excavation tasks?
Gas-powered trench diggers are equipped with powerful engines that excel in digging deep and wide trenches, making them efficient for extensive trenching tasks.
What are the pros and cons of gas-powered trench diggers?
Pros include faster operation that enhances project timelines, while cons include being heavier than manual options, requiring fuel, and potentially incurring higher maintenance costs.
What are the benefits of electric handheld trench diggers?
Electric trench diggers are quieter, environmentally friendly, have low emissions, and are easy to start, making them suitable for indoor work or noise-sensitive areas.
What limitations do electric handheld trench diggers have?
They are limited by cord length, which can restrict mobility, and may not deliver the same power levels as gas models in demanding conditions.
Why are hydraulic handheld trench diggers considered advanced tools?
Hydraulic trench diggers utilize hydraulic power to enhance digging efficiency, particularly in difficult soil conditions, allowing for precise excavation in various terrains.
What are the pros and cons of hydraulic handheld trench diggers?
Pros include high efficiency and the ability to handle tough soil, while cons typically involve higher costs and the need for specialized training for operators.
What safety guidelines should be followed when using handheld trench diggers?
Key guidelines include wearing proper safety gear, reading the manual, checking ground conditions, planning the digging path, maintaining a steady pace, taking breaks, and cleaning and maintaining the digger after use.




